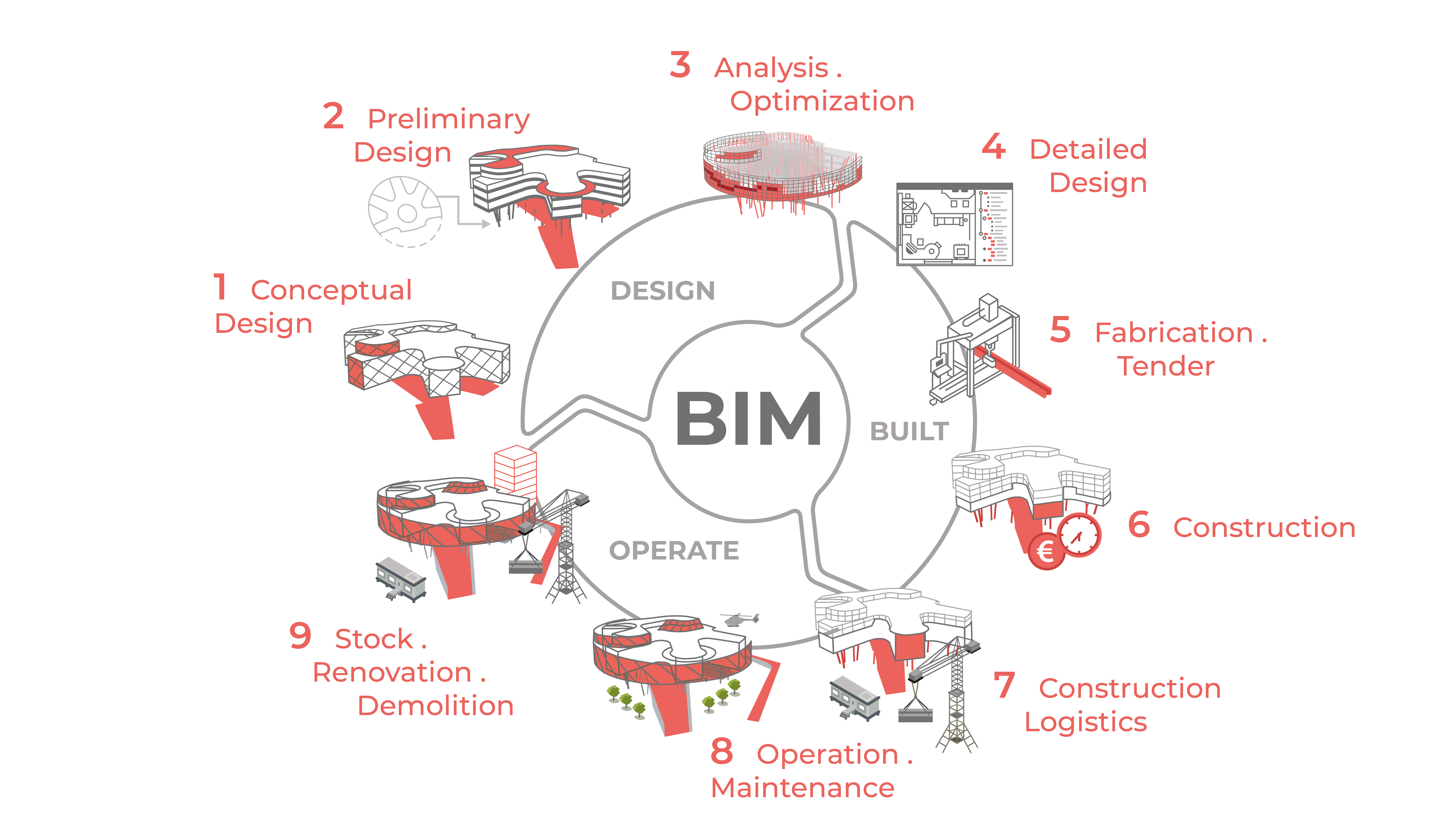
BIM . Building Information Modeling
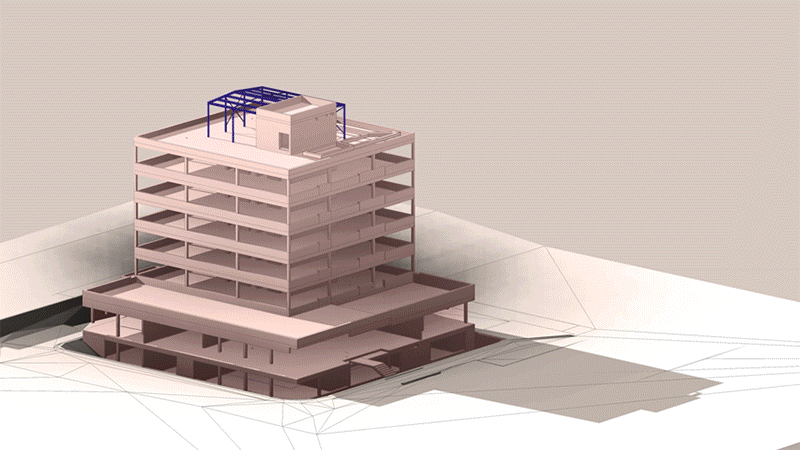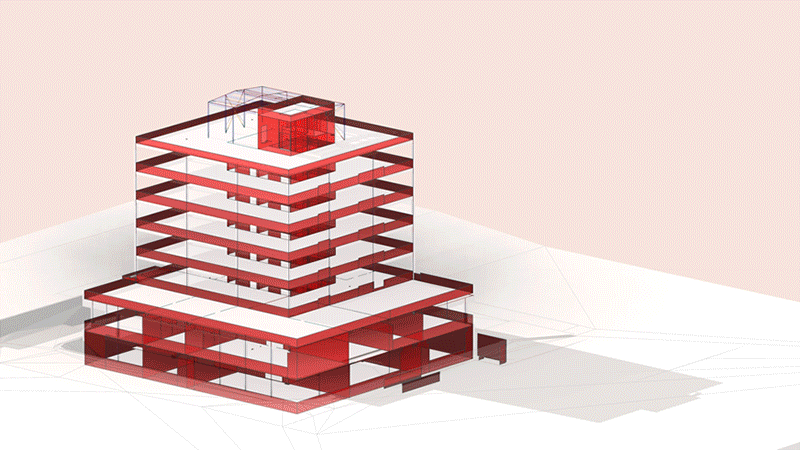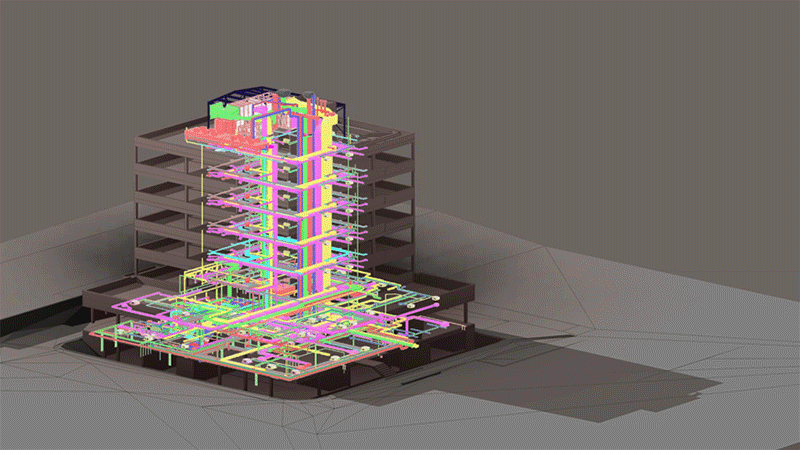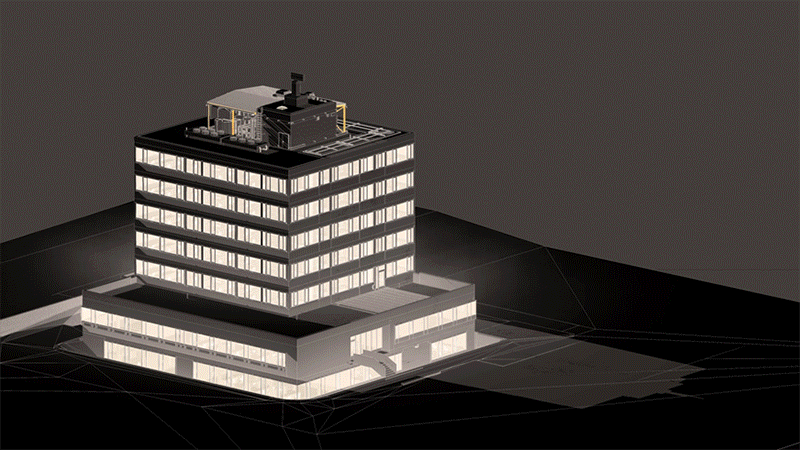
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a method of optimized design, implementation and management of buildings and projects. BIM tries to link heterogeneous and increasingly complex data amounts of all disciplines involved to establish a consistent database which is available any time and globally and quickly provides all information required.
Conceptual Design
1
⟩ BIM supports the planning process from the idea up to the completed project
⟩ integral planning from the beginning
⟩ additional work and expenses pay off and prevent later costly corrections
Preliminary Design
2
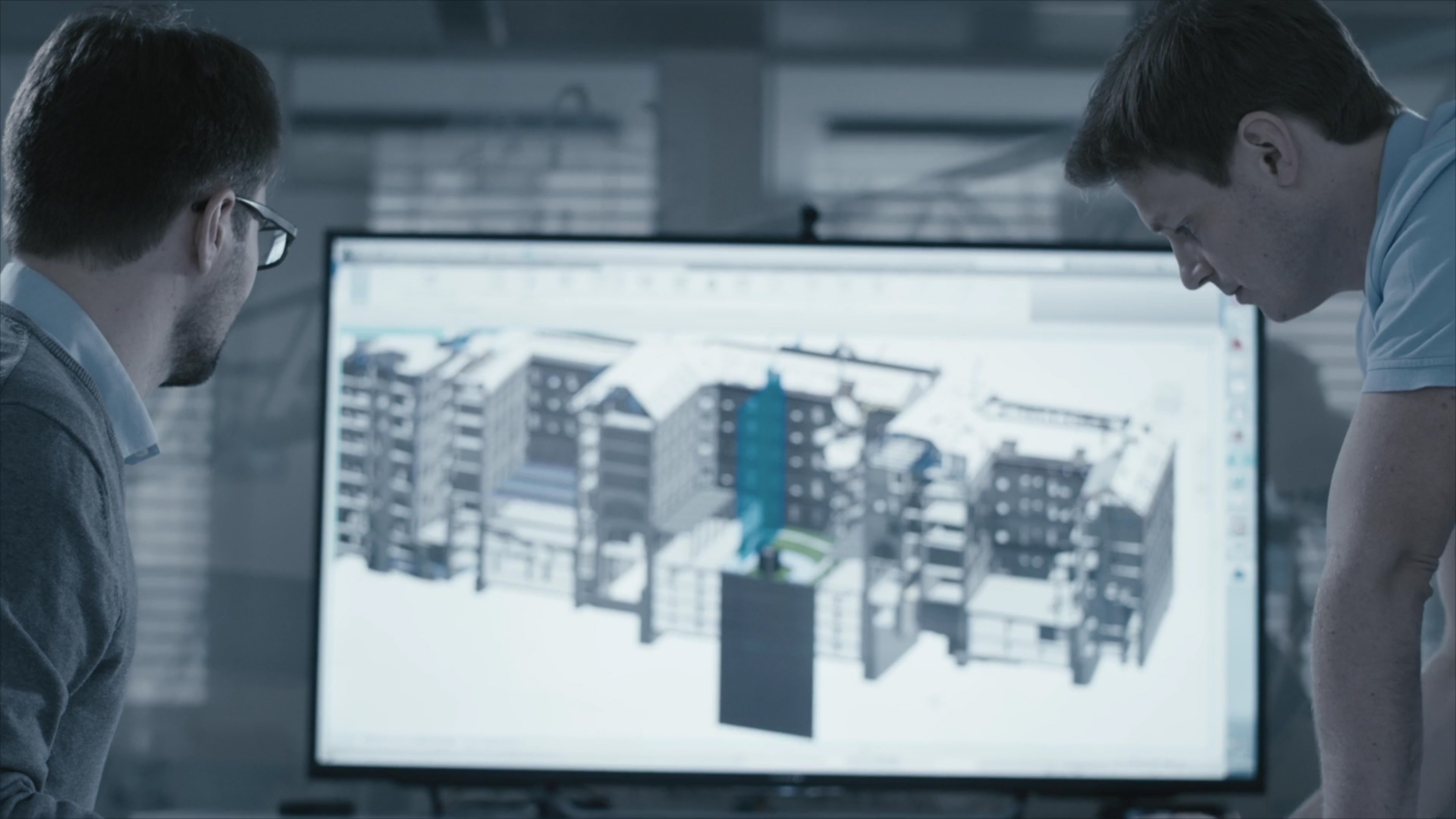
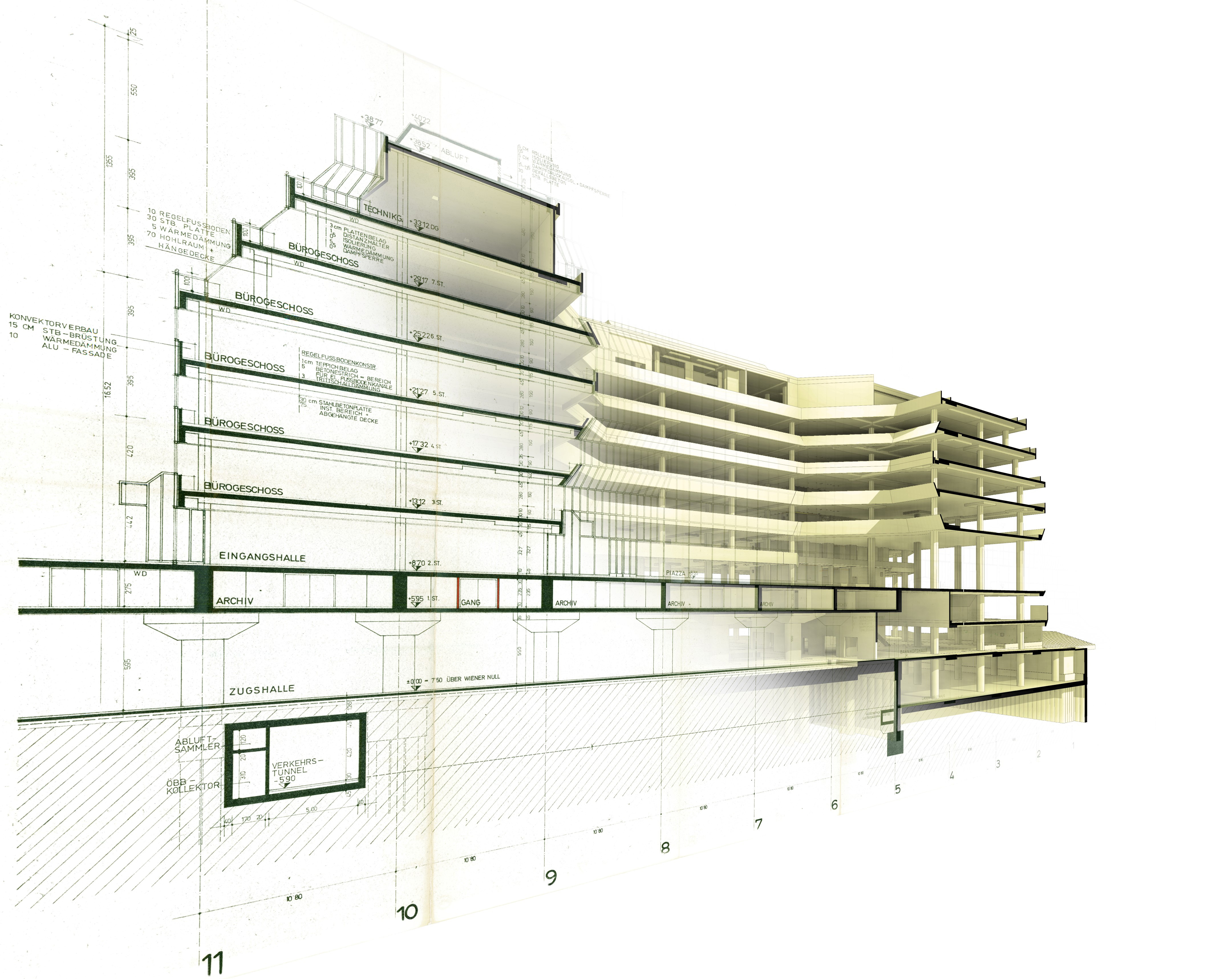
⟩ BIM model as optimum basis for discussion
⟩ realistic representation of the design
⟩ a BIM model supports planning of assets
⟩ planning quality is increased by the preparation of scatter plots
Analysis & Optimization
3
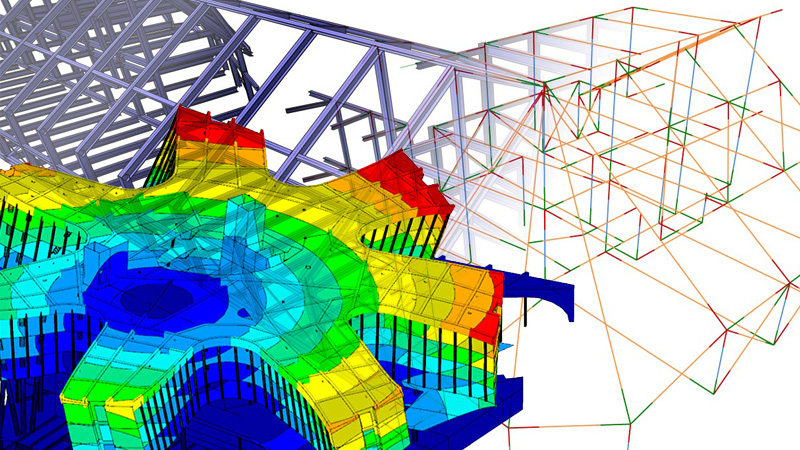
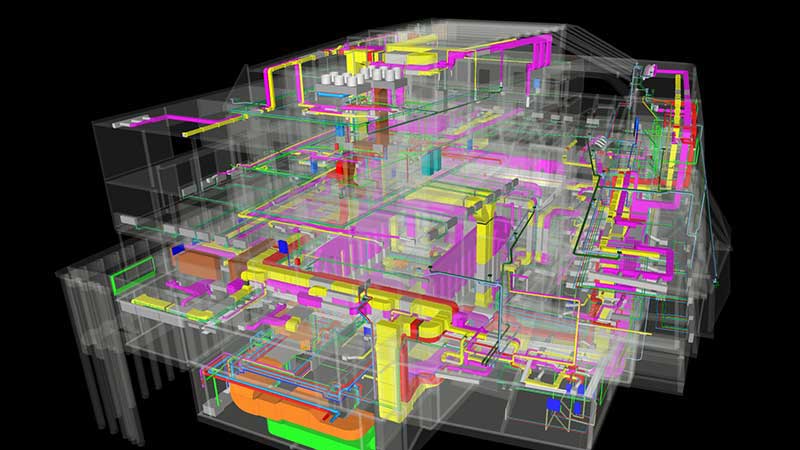
⟩ structures can be dimensioned and optimized by means of direct interfaces
⟩ BIM supports seismic calculations of existing buildings
⟩ structures can be simulated in advance by augmented and virtual reality
⟩ ideal representation of complex issues by augmented reality
Detailed Design
4
⟩ complex structures are registered and provide an optimum basis for the further process
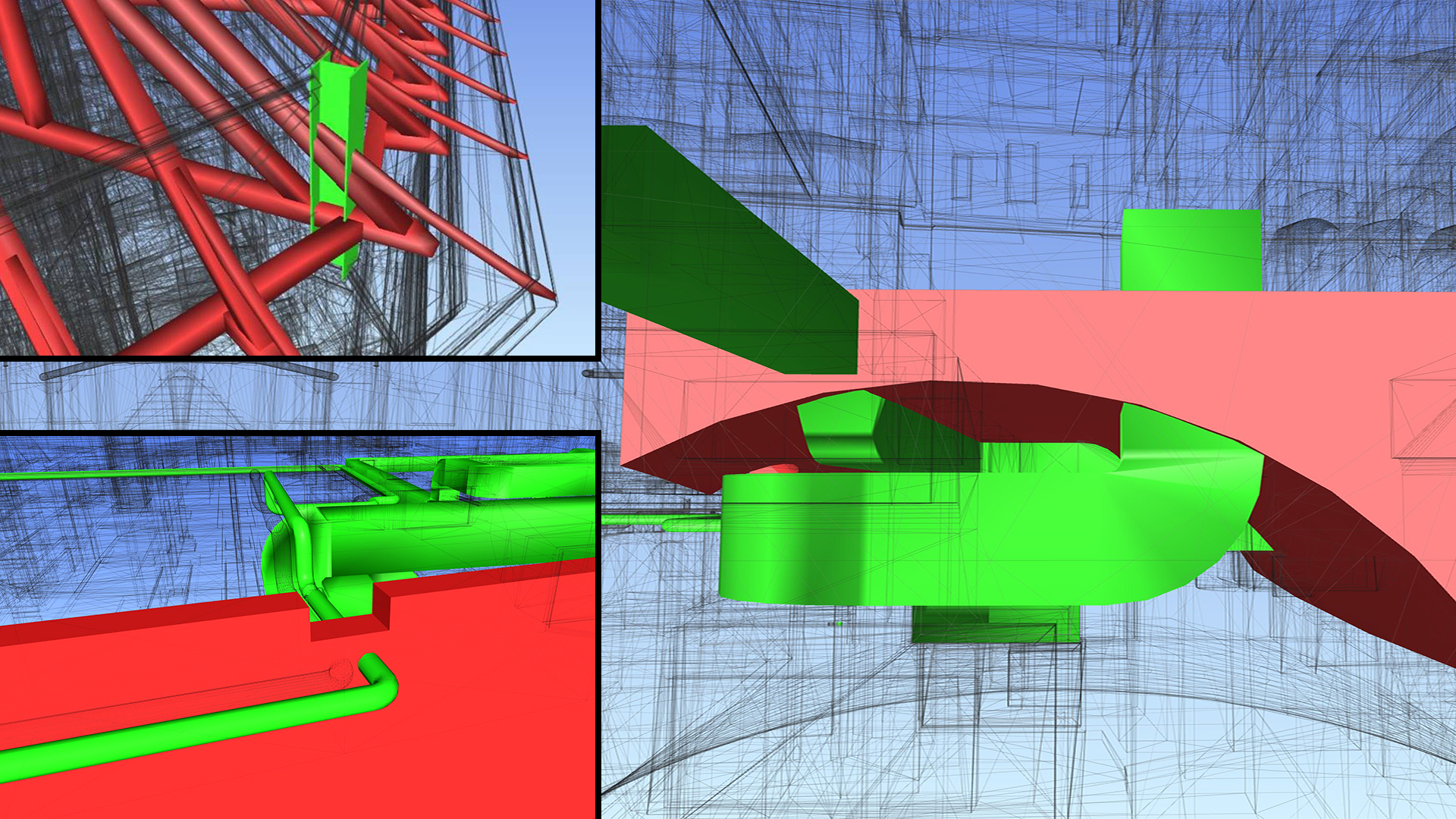
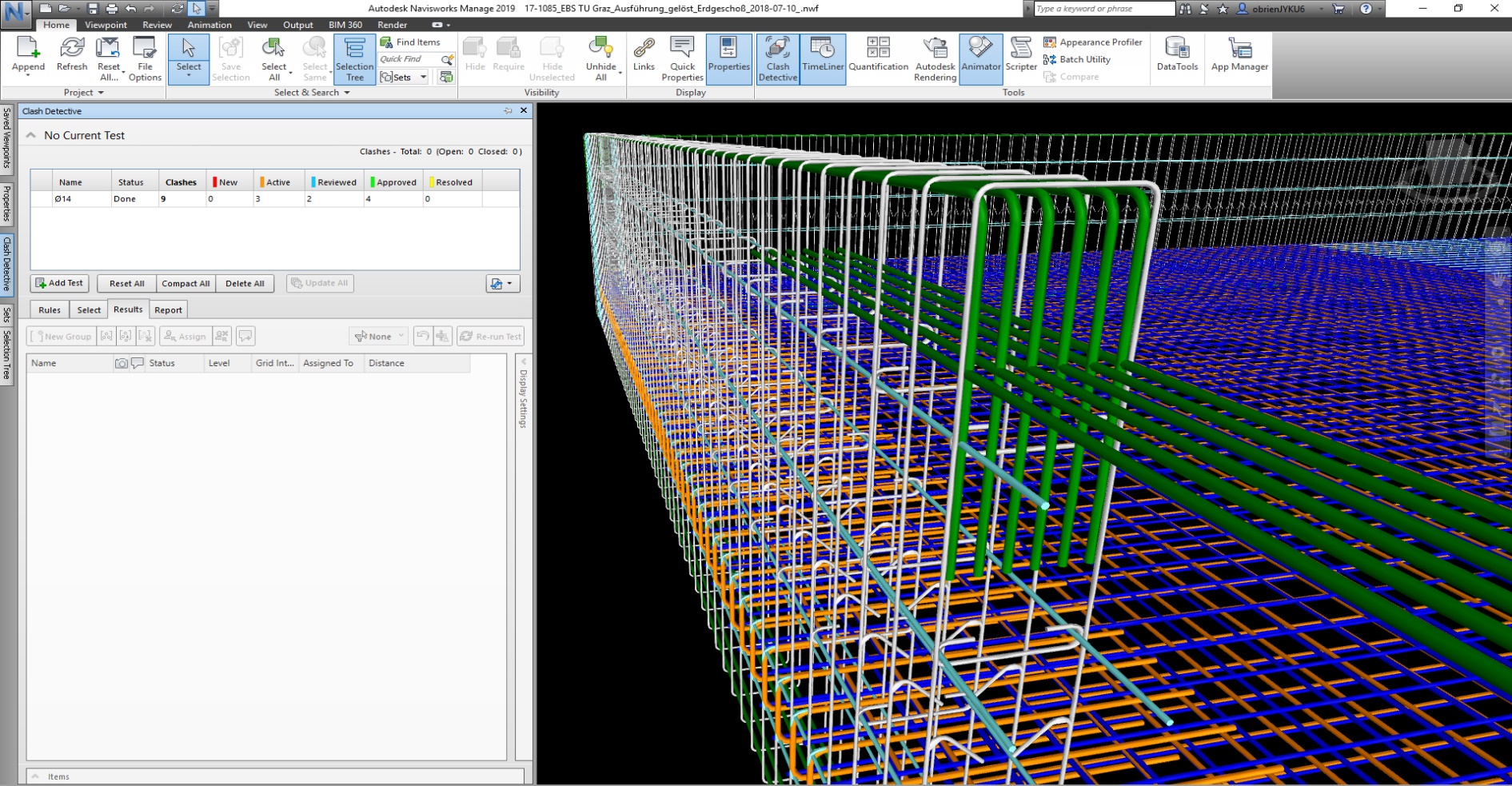
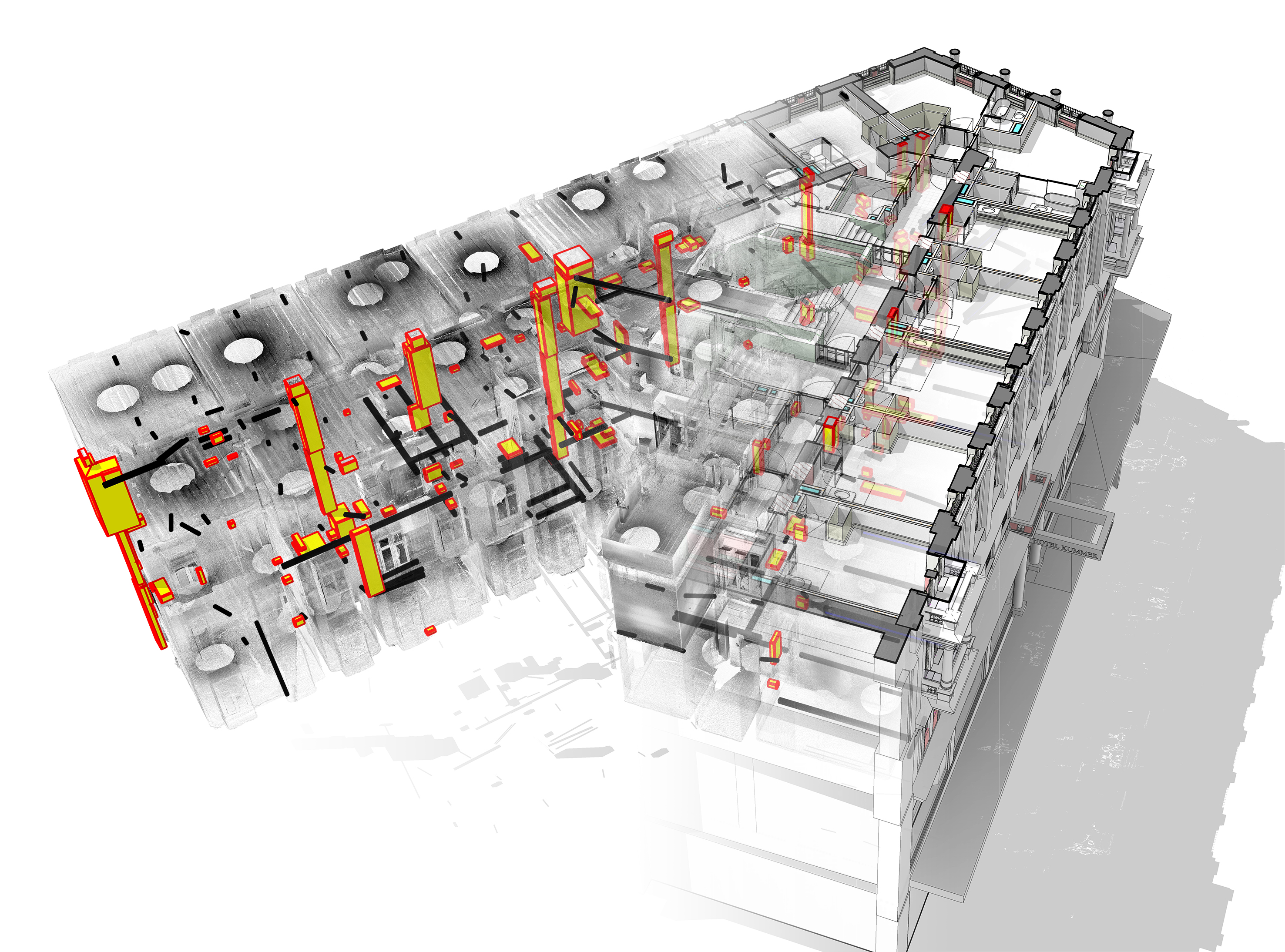
⟩ considerable increase in planning quality by collision checks
⟩ model-based plans ensure that layouts, sections and views are constantly harmonized with each other
⟩ feasibility of reinforcement is checked in the BIM model
Fabrication & Tender
5
⟩ BIM enables reliable solutions of complex geometries
⟩ BIM as a basis for construction and assembly design
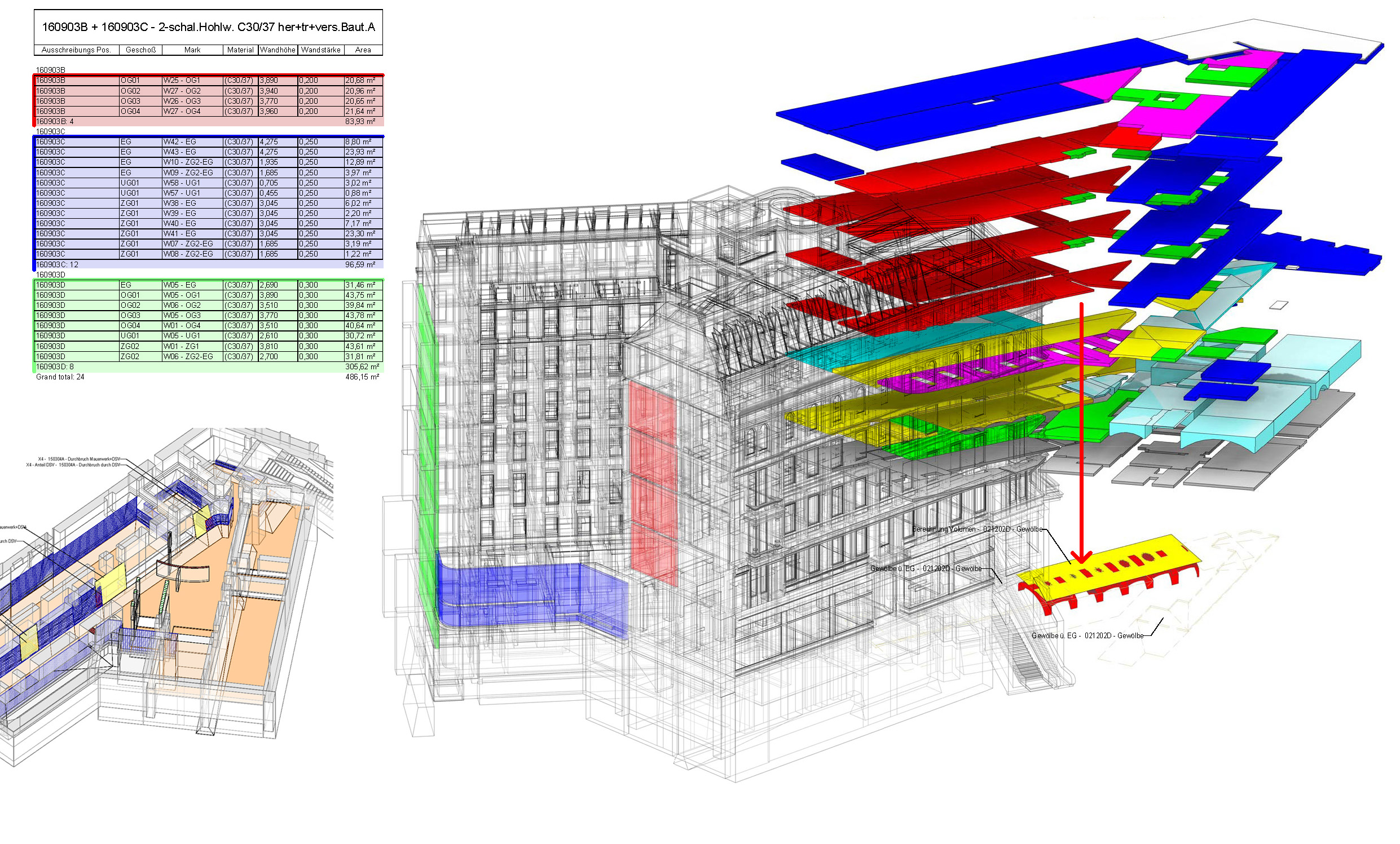
⟩ masses & costs can be continuously followed
⟩ masses direct and traceable by optic support
Construction
6
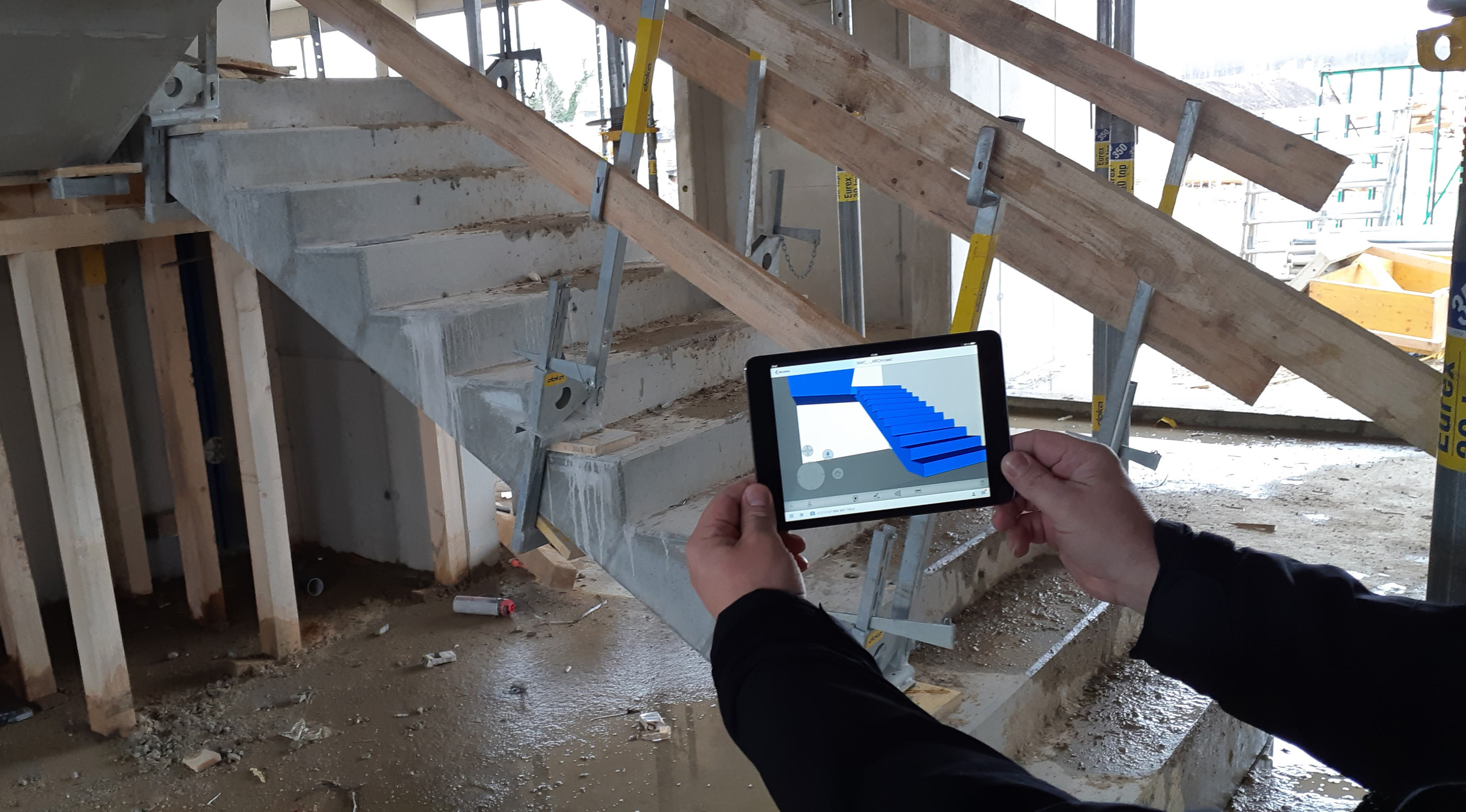
⟩ mobile utilization of the BIM model directly on the building site
⟩ check and optimization of the construction processes at the BIM model
⟩ masses & augmented reality support installation or acceptance of reinforcement
⟩ future-oriented settlement directly via the BIM model
Construction Logistics
7
⟩ check and optimization of construction progresses ensure an efficient building site
⟩ tracking of the construction progress by means of scatter plots during construction
⟩ implementation of the construction schedule (4D) into the BIM model
⟩ check and optimization of the logistic processes at the BIM model
Operation & Maintenance
8
⟩ recording of all relevant components for facility management
⟩ upgrading of the BIM model when used for facility/asset management
⟩ measurement results from structural monitoring are integrated into the BIM asset model
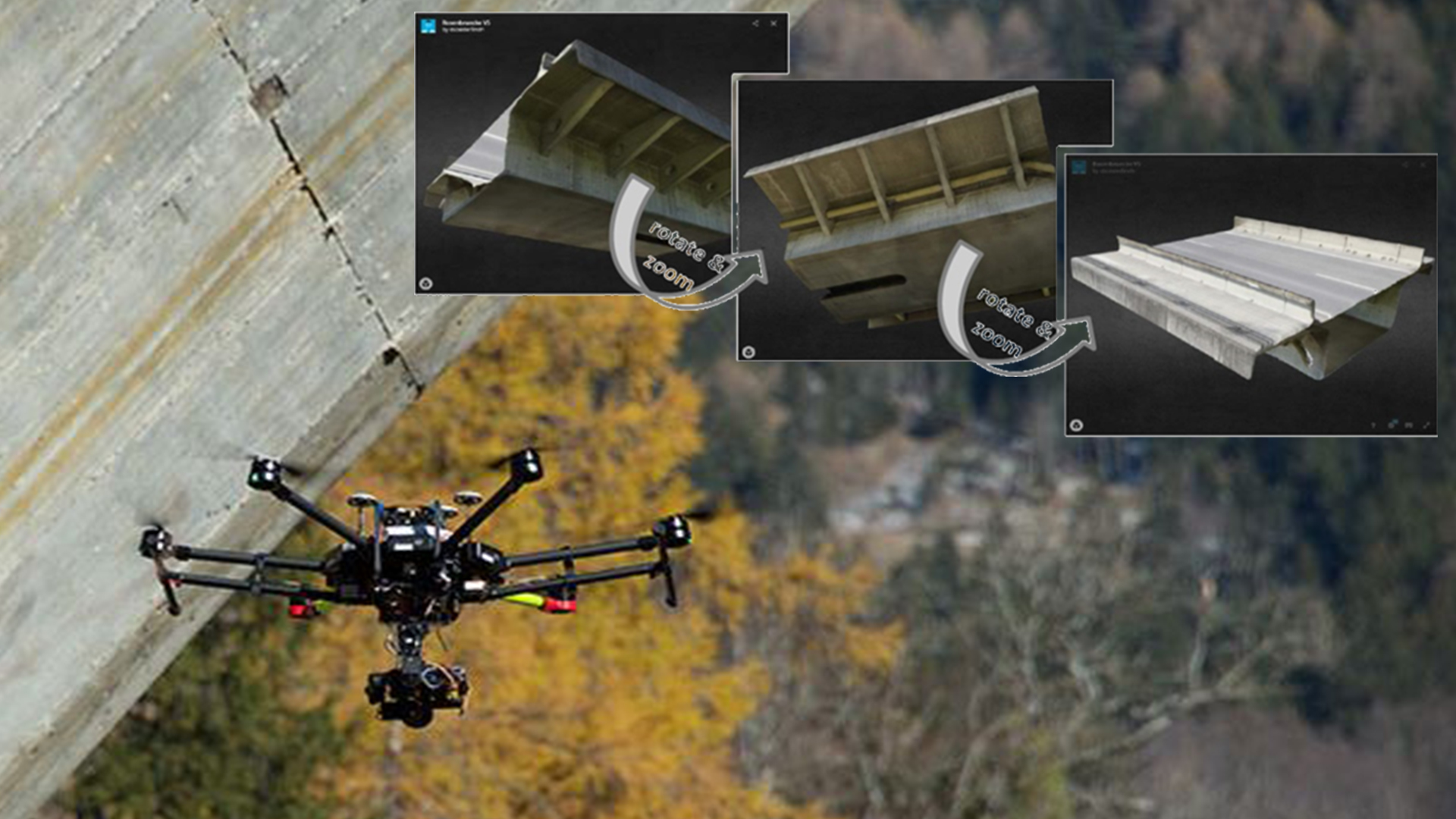
⟩ simplification of inspections by means of drone recordings
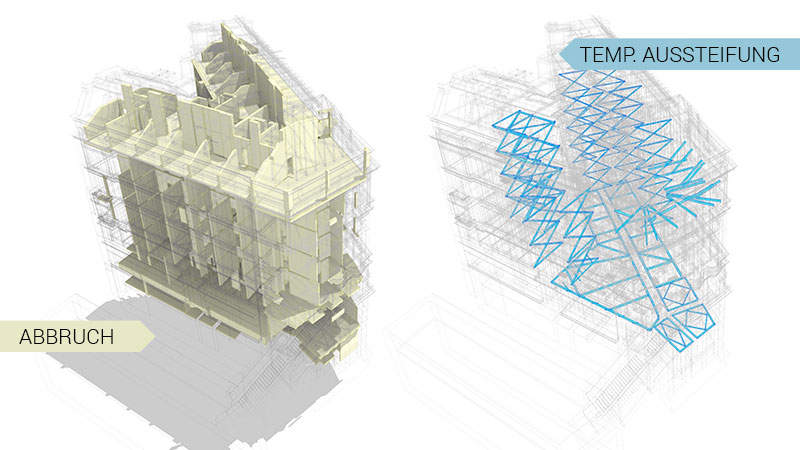
Stock . Renovation . Demolition
9